Oli Engine 9.3 Reference Manual
Generate and Equilibrium
Table of Contents
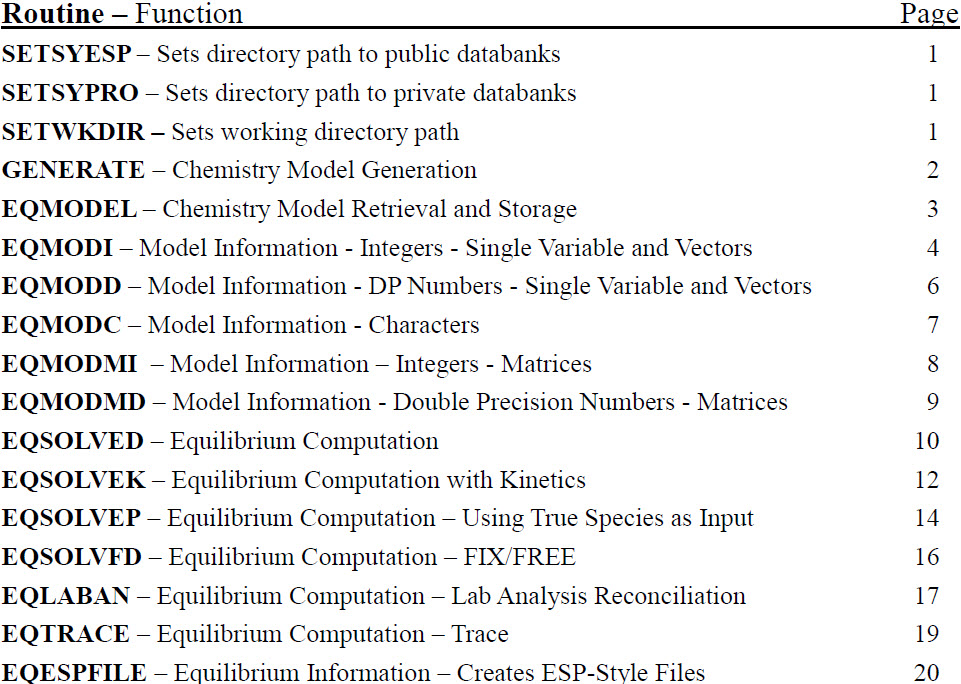
SETSYESP – Sets directory path to public databanks
SETSYPRO – Sets directory path to private databanks
SETWKDIR – Sets working directory path
Chemistry Model Path Setup
Calling SETSYESP sets the directory path to the public databanks. Calling SETSYPRO sets an alternate directory for finding private databanks. Calling SETWKDIR sets a directory path for any files created. These must be called before any other Model Information calls.
CALL SETSYESP (PATH)
CALL SETSYPRO (PATH)
CALL SETWKDIR (PATH)
Input:
PATH = Directory path to be set.
Output:
None
Example: SETSYESP ("d:\v60dev\esp")
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 2
GENERATE – Chemistry Model Generation
SETSYESP & SETSYPRO must be called before any of the Model Generation calls. GENERATE resets the Error storage by calling CLRERR.
Reads .mod file and creates .dbs file.
CALL GENERATE (MODNAM, DBNAM, NERRORS)
Input:
MODNAM = Model name (will be used to access MODNAM.mod file and write
MODNAM.dbs file) (single entry, CHARACTER*80)
DBNAM(I), I=1,5 = Database Names (CHARACTER*8)
Output:
NERRORS = Number of Errors or Warnings Encountered (Use GETERR to determine Error codes and statements)
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 3
EQMODEL – Chemistry Model Retrieval and Storage
Initialization
Reads .dbs file. Should be called only once. EQMODEL resets the Error storage by calling CLRERR.
CALL EQMODEL (MODNAM, NERRORS)
Input:
MODNAM = Model name (will be used to access MODNAM.dbs file) (single entry, CHARACTER variable)
Output:
NERRORS = Number of Errors or Warnings Encountered (Use GETERR to determine Error codes and statements)
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 4
EQMODI – Model Information - Integers - Single Variable and Vectors
EQMODEL must be called before any of the Model Information calls.
CALL EQMODI (IVALI, NVALI, NVEC, IERR)
Input:
IVALI = ID number of integer vector to be returned
Output:
NVALI = Number of integer values in NVEC vector
NVEC = Vector of integer values
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized
IVALI NVALI Maximum NVEC(I), I = 1 , NVALI
1 1 1 Number of Inflows (NI)
2 1 1 Number of Species (NU)
3 1 1 Number of Material Balance Groups (NMOLIN, NMATYP)
4 1 1 Number of Scale Solid Names
(NSNAME)
5 1 1 Number of K-Values (NK)
6 1 1 Number of Activities/Activity Coefficients (NA)
7 1 1 Number of ASAP Variables (N(1))
8 1 1 Number of Vapors (NP)
9 1 1 Maximum Length of ESTREA vector (LQESTR)
10 1 1 Number of Equilibrium-Kinetics Reactions (NKINADD)
11 1 1 Maximum Number of Species/Inflows (NNSP)
101 1 1 Redox Flag
NVEC(1) = 0 for No Redox Equations present in Model
= 1 for Redox Equations present in Model
1001 NU NNSP Species Type, Species I
NVEC(I) = 1 for H2O
= 2 –AQ
= 3 –ION
= 4 –PPT
= 5 –.nH2O
= 6 –VAP
= 7 –SOL
= 9 –SUS
=10 –LT
=11 –CPI
=12 –CPM
1002 NU NNSP Inflow Number corresponding to Species I
1003 NI NNIN Species Number corresponding to Inflow I
1004 NMOLIN NMOLIN Material Balance Group Numbers (MOLIN)
corresponding to names (NAMMOL)
Note: NMATYP=NMOLIN and MOLIN(I)=MATYP(I)
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 5
EQMODI – Model Information - Integers - Single Variable and Vectors (cont.)
CALL EQMODI (IVALI, NVALI, NVEC, IERR)
IVALI NVALI Maximum NVEC(I), I = 1 , NVALI
1005 NK NNKEQN Species Number corresponding to K-Value I (NKLOC)
1006 NKINADD NNREAC Species Numbers of species associated with
Equilibrium-Kinetics Reaction I (ISPEQ)
2001 12 12 IGC vector- molecular stream (GVEC)
output vector pointers
2002 1 1 LQGSTR – maximum length of molecular stream
(GVEC) output vector
2003 1 1 LQESTR – maximum length of ionic stream (EVEC)
output vector
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 6
EQMODD – Model Information - DP Numbers - Single Variable and Vectors
EQMODEL must be called before any of the Model Information calls.
CALL EQMODD (IVALR, NVALR, VEC, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
IVALR = ID number of real number vector to be returned
Output:
NVALR = Number of real number values in VEC vector
VEC = Vector of real number values (REAL*8)
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized
IVALR NVALR Maximum VEC(I), I = 1, NVALR
1 NU NNSP Species Charge, Species I (ZERM)
2 NI NNIN Molecular Weight, Inflow I (AMWIN)
3 NU NNSP Molecular Weight, Species I (AMWSPE)
4 NMOLIN NNMOLT Molecular Weight, MB Group I (AMWMB)
Note: NMATYP = NMOLIN
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 7
EQMODC – Model Information - Characters
EQMODEL must be called before any of the Model Information calls.
CALL EQMODC (INAME, NNAME, NAME, IERR)
Input:
INAME = ID number of names vector to be returned
Output:
NNAME = Number of names in NAME vector
NAME = Vector of names
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized
INAME NNAME Maximum NAME(I), I = 1, NNAME
1 NI NNIN Inflow Name, Inflow I (“molecular species") with IN suffix (SPNAME)
2 NI NNIN Inflow Name, Inflow I (“molecular species") without IN suffix (SPNAMS)
3 NU NNSP Species Names ("solution species") (VNAME)
4 NSNAME NNSOLI Scale Solid Names (SNAME)
5 NMOLIN NNMOLT MB Group Names (NAMMOL)
Note: NMATYP = NMOLIN
6 NK NNKEQN K-Value Names (AKNAME)
7 NA NNSP Activity/Activity Coefficient Names (ACTNAM)
8 N(1) NNVAR ASAP Variable Names (NAMEV)
9 NP NNVAP Vapor Names (as they appear in VNAME(2 to NP+1)
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 8
EQMODMI – Model Information – Integers - Matrices
EQMODEL must be called before any of the Model Information calls.
CALL EQMODMI (IVALI, IRC,NRC,NVALI, NVEC, IERR)
Input:
IVALI = ID number of integer vector to be returned
IRC = Row or Column Designation [MATRIX(Row, Column)]
= 1 for Row designation
= 2 for Column designation
NRC = Number of Row or Column to be returned as a vector
Output:
NVALI = Number of integer values in NVEC vector
NVEC = Vector of integer values
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized
For example, for IVALI=1 (i.e., NICOMP(NNMATC, NI))
if IRC=2 (Column designation)
and NRC=3 (return column number 3)
then NVEC(1- NNMATC) = NICOMP(1- NNMATC, 3) (i.e., The first
NNMATC MB group ID entries for Inflow Number 3)
IVALI NVALI Maximum NVEC(I), I = 1 , NVALI
1 NI NNIN NICOMP(NNMATC,NI)
2 NU NNSP NCOMP(NNMATC,NU)
3 NK when IRC=1 NNKEQN KVAL(10,NK) (Reactants<0,
No. of Species when IRC=2 10 KVAL(10,NK) Products>0)
4 NI NNIN MICOMP(NNMATC,NI)
MICOMP(J,I) = location of Jth MB
Group of Inflow I in the list of MB Group Numbers (MOLIN)
5 NU NNSP MCOMP(NNMATC,NI)
MCOMP(J,I) = location of Jth MB
Group of Species I in the list of MB Group Numbers (MOLIN)
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 9
EQMODMD – Model Information - Double Precision Numbers - Matrices
EQMODEL must be called before any of the Model Information calls.
CALL EQMODMD (IVALR, IRC,NRC,NVALR, VEC, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
IVALR = ID number of real vector to be returned
IRC = Row or Column Designation
= 1 for Row designation
= 2 for Column designation
NRC = Number of Row or Column to be returned as a vector
Output:
NVALR = Number of integer values in NVEC vector
VEC = Vector of real values (REAL*8)
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized
For example, for IVALR=1 (i.e., CIROMP(5, NI))
if IRC=2 (Column designation)
and NRC=3 (return column number 3)
then VEC(1-5) = CIROMP(1-5, 3) (i.e., The first 5 MB group
stoichiometric coefficients for Inflow Number 3)
IVALI NVALI Maximum NVEC(I), I = 1 , NVALI
1 NI NNSP CIROMP(NNMATC,NI)
2 NU NNIN CROMP(NNMATC,NU)
3 NK when IRC=1 NNKEQN RCVAL(10,NK) (Reactants<0,
No. of Species when IRC=2 10 RCVAL(10,NK) Products>0)
4 NU when IRC=1 NNSP TRANGE(2,NU)
2 when IRC=2 2
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 10
EQSOLVED – Equilibrium Computation
Computes equilibrium condition and retains results in Solver. Until EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN is called again, the results remain stored and in effect. EQSOLVED may be called as often as necessary.
CALL EQSOLVED (IFUNC, IREST, TEMP, PRES, COMP, NSPEC, SPEC, JSOLID, NIPROP, IPROP, EVEC, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
IFUNC = Function (see below)
IREST = Restart indicator
= 0 initialization of equilibrium calculation by ESP
= 1 use the values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
= 2 use only the non-zero values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
(i.e., “Guesses” for selected species)
TEMP = Temperature, C (REAL*8)
PRES = Pressure, atm (REAL*8)
COMP(I), I=1,NI = Inflows, gmole/hr (REAL*8)
NSPEC = The number of SPEC variables
SPEC(I), I=1,NSPEC = Equilibrium specification values - ONLY entered for
some Functions (see below) (REAL*8)
JSOLID(I), I=1,NU = Inclusion indicators for solids in equilibrium calculation
= 0 include species I (a solid) in equilibrium calculation
= 1 exclude species I (a solid) from consideration
NIPROP = The number of IPROP specifications
IPROP(I) = Property calculation flag.
0 – Do not calculate the following properties (default)
1 – Calculate Electrical Conductivity
2 – Calculate Viscosity
3 – Calculate Diffusivity
4 – Calculate Heat Capacity
98 – Calculate 1 – 2 - 3
99 – Calculate all of the above properties
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order; used
to fill BSTSAV in restart cases) (REAL*8)
Output:
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order) (REAL*8)
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
> 0 Error encountered
Functions
Specifications
Function Type SPEC(1) SPEC(2) SPEC(3) Compute
1 T, P -- --
2 T, Bubble -- P
3 P, Bubble -- T
4 T, Dew -- P
5 P, Dew -- T
6 T, Vapor V (gmol) P
7 P, Vapor V (gmol) T
8 T, V/F V/F (frac) P
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 11
9 P, V/F V/F (frac) T
10 T,LIQMOL LIQMOL P
11 P,LIQMOL LIQMOL T
12 P, H H (cal) T
15 T, P, pH pH Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
16 T, P, Precip Pt Sp # of Precip Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
17 T, P, Composi Composi (mole fr) Sp # Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
18 T, P, Volume Volume (m3) FRAC (H2O Inflow)
21 Volume, H Volume(m3) H (cal) T, P
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 12
EQSOLVEK – Equilibrium Computation with Kinetics
Until EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN is called again, the results remain stored and in effect. EQSOLVEK may be called as often as necessary.
CALL EQSOLVEK (IFUNC, IREST, TEMP, PRES, COMP, NSPEC, SPEC, JSOLID, NIPROP, IPROP, HOLDUP, KISTEP, EVECIN, EVEC, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
IFUNC = Function (see below)
IREST = Restart indicator
= 0 initialization of equilibrium calculation by ESP
= 1 use the values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
= 2 use only the non-zero values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
(i.e., “Guesses” for selected species)
TEMP = Temperature, C (REAL*8)
PRES = Pressure, atm (REAL*8)
COMP(I), I=1,NI = Inflows, gmole/hr (REAL*8)
NSPEC = The number of SPEC variables
SPEC(I), I=1,NSPEC = Equilibrium specification values - ONLY entered for
some Functions (see below) (REAL*8)
JSOLID(I), I=1,NU = Inclusion indicators for solids in equilibrium calculation
= 0 include species I (a solid) in equilibrium calculation
= 1 exclude species I (a solid) from consideration
NIPROP = The number of IPROP specifications
IPROP(I) = Property calculation flag.
0 – Do not calculate the following properties (default)
1 – Calculate Electrical Conductivity
2 – Calculate Viscosity
3 – Calculate Diffusivity
4 – Calculate Heat Capacity
98 – Calculate 1 – 2 - 3
99 – Calculate all of the above properties
HOLDUPT = Residence time for Kinetics, hr (REAL*8)
KISTEP = Number of CSTR reactors, residence time in each = HOLDUPT / KISTEP
EVECIN(J), J=1,NKINADD = Reactor true species feed rate, gmole/hr (For species
VNAME(ISPEQ(J) ) (REAL*8)
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order; used
to fill BSTSAV in restart cases) (REAL*8)
Output:
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order) (REAL*8)
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
> 0 Error encountered
Functions
Specifications
Function Type SPEC(1) SPEC(2) SPEC(3) Compute
1 T, P -- --
2 T, Bubble -- P
3 P, Bubble -- T
4 T, Dew -- P
5 P, Dew -- T
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 13
6 T, Vapor V (gmol) P
7 P, Vapor V (gmol) T
8 T, V/F V/F (frac) P
9 P, V/F V/F (frac) T
10 T,LIQMOL LIQMOL P
11 P,LIQMOL LIQMOL T
12 P, H H (cal) T
15 T, P, pH pH Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
16 T, P, Precip Pt Sp # of Precip Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
17 T, P, Composi Composi (mole fr) Sp # Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
18 T, P, Volume Volume (m3) FRAC (H2O Inflow)
21 Volume, H Volume(m3) H (cal) T, P
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 14
EQSOLVEP – Equilibrium Computation – Using True Species as Input
Computes equilibrium condition and retains results in Solver. Until EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN is called again, the results remain stored and in effect. EQSOLVEP may be called as often as necessary.
CALL EQSOLVEP (IFUNC, IREST, TEMP, PRES, COMP, NSPEC, SPEC, JSOLID, NIPROP, IPROP, EVEC, IBERR, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
IFUNC = Function (see below)
IREST = Restart indicator
= 0 initialization of equilibrium calculation by ESP
= 1 use the values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
= 2 use only the non-zero values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
(i.e., “Guesses” for selected species)
TEMP = Temperature, C (REAL*8)
PRES = Pressure, atm (REAL*8)
COMP(I), I=1,NU = Species, gmole/hr (VNAME order; REAL*8)
NSPEC = The number of SPEC variables
SPEC(I), I=1,NSPEC = Equilibrium specification values - ONLY entered for
some Functions (see below) (REAL*8)
JSOLID(I), I=1,NU = Inclusion indicators for solids in equilibrium calculation
= 0 include species I (a solid) in equilibrium calculation
= 1 exclude species I (a solid) from consideration
NIPROP = The number of IPROP specifications
IPROP(I) = Property calculation flag.
0 – Do not calculate the following properties (default)
1 – Calculate Electrical Conductivity
2 – Calculate Viscosity
3 – Calculate Diffusivity
4 – Calculate Heat Capacity
98 – Calculate 1 – 2 - 3
99 – Calculate all of the above properties
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order; used
to fill BSTSAV in restart cases) (REAL*8)
Output:
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order; REAL*8)
IBERR = 0 No errors encountered
> 0 Error encountered in Material Balance redistribution
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
> 0 Error encountered
Functions
Specifications
Function Type SPEC(1) SPEC(2) SPEC(3) Compute
1 T, P -- --
2 T, Bubble -- P
3 P, Bubble -- T
4 T, Dew -- P
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 15
5 P, Dew -- T
6 T, Vapor V (gmol) P
7 P, Vapor V (gmol) T
8 T, V/F V/F (frac) P
9 P, V/F V/F (frac) T
10 T,LIQMOL LIQMOL P
11 P,LIQMOL LIQMOL T
12 P, H H (cal) T
15 T, P, pH pH Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
16 T, P, Precip Pt Sp # of Precip Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
17 T, P, Composi Composi (mole fr) Sp # Inflow # FRAC (Inflow)
18 T, P, Volume Volume (m3) FRAC (H2O Inflow)
21 Volume, H Volume (m3) H (cal) T,P
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 16
EQSOLVFD – Equilibrium Computation – FIX/FREE
Computes equilibrium condition and retains results in Solver. Until EQSOLVFD is called again, the results remain stored and in effect. EQSOLVFD may be called as often as necessary.
CALL EQSOLVFD (NFIXFR, IREST, TEMP, PRES, COMP, JSOLID, NIPROP, IPROP,
NAMFIX, VALFIX, NAMFRE, VALFRE, EVEC, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
NFIXFR = Number of FIXed/FREEed Variables (Maximum = LQFXFR = 10)
IREST = Restart indicator
= 0 initialization of equilibrium calculation by ESP
= 1 use the values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
= 2 use only the non-zero values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
(i.e., “Guesses” for selected species)
TEMP = Temperature, C (REAL*8)
PRES = Pressure, atm (REAL*8)
COMP(I), I=1,NI = Inflows, gmole/hr (REAL*8)
JSOLID(I), I=1,NU = Inclusion indicators for solids in equilibrium calculation
= 0 include species I (a solid) in equilibrium calculation
= 1 exclude species I (a solid) from consideration
NIPROP = The number of IPROP specifications
IPROP(I) = Property calculation flag.
0 – Do not calculate the following properties (default)
1 – Calculate Electrical Conductivity
2 – Calculate Viscosity
3 – Calculate Diffusivity
4 – Calculate Heat Capacity
98 – Calculate 1 – 2 - 3
99 – Calculate all of the above properties
NAMFIX(I), I=1,NFIX = Names of Variables to be FIXed (CHARACTER*16)
VALFIX(I), I=1,NFIX = Values of FIXed Variables (REAL*8)
NAMFRE(I), I=1,NFIX = Names of Variables to be FREEed (CHARACTER*16)
VALFRE(I), I=1,NFIX = Initial Values of FREEed Variables (REAL*8)
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order; used
to fill BSTSAV in restart cases) (REAL*8)
Output:
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order) (REAL*8)
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 Error encountered
= 2 Error: NFIX not equal to NFREE
= 3 Error: An Illegal variable name has been entered as a FIXed variable
= 3 Error: An Illegal variable name has been entered as a FREEed variable
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 17
EQLABAN – Equilibrium Computation – Lab Analysis Reconciliation
Performs Laboratory Analysis reconciliation, computes equilibrium condition and retains results in Solver. The amount of water is determined based upon the specified concentrations. Until EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN is called again, the results remain stored and in effect. EQLABAN may be called as often as necessary.
CALL EQLABAN (IFUNC, IBALAN, ICAT, IANI, IREST, TEMP, PRES, CONC,
IUNCON, DENS, JSOLID, NIPROP, IPROP, EVEC, CONCADD, CONCOUT, COMPOUT, IERR) (Double Precision)
Input:
IFUNC = Computation Function (Currently Unused; all equilibrium computations are
“isothermal”)
IBALAN = Electroneutrality Reconciliation criterion
= 0 Dominant ion (default)
= 1 Prorate (i.e., add all ions of the necessary charge proportionally to the existing equivalents)
= 2 User choice (ICAT and IANI will contain species numbers)
= 3 Na+/Cl-
= 4 Makeup ion (One ion will be chosen. Its added amount may be negative o or positive)
ICAT = Species Number of Cation to be used for balancing (entered for IBALAN = 2
and 4)
IANI = Species Number of Anion to be used for balancing (entered for IBALAN = 2)
Note: When IBALAN=4, ICAT = IANI (thus IANI will be ignored)
IREST = Restart indicator
= 0 initialization of equilibrium calculation by ESP
= 1 use the values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
= 2 use only the non-zero values in EVEC to initialize the equilibrium calculation
(i.e., “Guesses” for selected species)
TEMP = Temperature, C (REAL*8)
PRES = Pressure, atm (REAL*8)
CONC(I), I=1,NU = Concentrations of solution species, mg/l (units in IUNCON except
H2O) (REAL*8)
IUNCON = Concentration units of CONC(2 to NU) - Currently unused, all units: mg/l
Note: CONC(1) = H2O guess (if zero, will be guessed using CONC and DENS)
DENS = Bulk Density GUESS, gm/ml (CONC(1) takes precedence over DENS guess)
JSOLID(I), I=1,NU = Inclusion indicators for solids in equilibrium calculation
= 0 include species I (a solid) in equilibrium calculation
= 1 exclude species I (a solid) from consideration
NIPROP = The number of IPROP specifications
IPROP(I) = Property calculation flag.
0 – Do not calculate the following properties (default)
1 – Calculate Electrical Conductivity
2 – Calculate Viscosity
3 – Calculate Diffusivity
4 – Calculate Heat Capacity
98 – Calculate 1 – 2 - 3
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 18
99 – Calculate all of the above properties
Output:
EVEC(I), I=1,LQESTR = Aqueous Stream Output Vector (VNAME order; used
to fill BSTSAV in restart cases) (REAL*8)
CONC(1) = H2O in IUNCON units (currently mg/l)
DENS = Bulk density, gm/ml
CONCADD(I), I=1,NU = Concentrations of solution species added to reconcile (units in
IUNCON – currently mg/l)
CONCOUT(I), I=1,NU = Concentrations of solution species after reconciliation (units in
IUNCON– currently mg/l)
COMPOUT(I), I=1,NI = Component Flows after reconciliation, gmole
IERR = 0 No errors encountered
= 1 IBALAN = 2 and ICAT = 0
= 2 IBALAN = 2 and IANI = 0
= 3 IBALAN = 3 and NAION not in model
= 4 IBALAN = 3 and CLION not in model
= 5 IBALAN = 4 and resulting flow is negative
= 6 Equilibrium computation did not converge
OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 19
EQTRACE – Equilibrium Computation – Trace
When an equilibrium computation is being done by EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN an ElectroChem-style output may be produced as a Trace to a disk file. EQTRACE opens the disk file with the Trace Disk File Name. The Trace Level sets the amount of information to be included in the file. EQTRACE should be called before the call to one of the computation routines. The Trace remains in effect until a call to EQCLOSE. Thus, a Trace file may contain multiple computations, the Trace outputs being concatenated in the file. EQCLOSE closes the Trace Disk File and terminates the Trace Level.
After EQCLOSE is called, EQTRACE may be called again with a different Trace Disk File Name to start writing the output to a new output file.
CALL EQTRACE (ITRACE, TRANAM)
- : : : : : :
Call(s) to Computatio Routines (EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN)
- : : : : : :
CALL EQCLOSE Input: ITRACE = Trace Level (0 to 8) = 0 Basic ElectroChem output = 8 Extensive debugging output including Jacobeans on each iteration TRANAM = Trace Disk File Name (The entire file name, including extension, should be included. For example, TRANAM=’case1.oue’) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 20 EQESPFILE – Equilibrium Information – Creates ESP-Style Files EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN must be called before any of the Equilibrium Information calls. CALL EQESPFILE (IFUNC, FILENAM, MODELNAM, STRMNAM, IERR) Input: IFUNC = File Creation Function = 1 create a FILENAM.bst file = 2 create a FILENAM.bin file = 3 create a FILENAM.bst file and FILENAM.bin file FILENAM = Filename of ESP-style output file MODELNAM = Name of the Chemistry Model to be entered under $MODEL (should not have an extension such as .mod) STRMNAM = Stream Name to be entered under $STREAM Output: IERR = 0 No errors encountered = 1 Error encountered OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 21 EQSOLI – Equilibrium Information – Integers EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN must be called before any of the Equilibrium Information calls. CALL EQSOLI (IVALI, NVALI, NVEC, IERR) Input: IVALI = ID number of integer vector to be returned Output: NVALI = Number of integer values in vector NVEC = Vector of integer values IERR = 0 No errors encountered = 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized IVALI NVALI Maximum NVEC(I), I = 1 , NVALI 1 1 1 Debug Index (IDEBUG) 2 1 1 I/O Unit being used for Output (LCFILO) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 22 EQSOLD – Equilibrium Information – Double Precision Numbers EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN must be called before any of the Equilibrium Information calls CALL EQSOLD (IVALR, NVALR, VEC, IERR) (Double Precision) Input: IVALR = ID number of real number vector to be returned Output: NVALR = Number of real number values in vector VEC = Vector of real number values (REAL*8) IERR = 0 No errors encountered = 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized IVALR NVALR Maximum VEC(I), I = 1 , NVALR 1 1 1 Temperature, C 2 1 1 Pressure, atm 3 1 1 pH 4 1 1 Total Enthalpy, cal 5 1 1 Total Volume, m3 6 1 1 Total Mass, gmole 7 1 1 Total Mass, grams 8 1 1 Ionic Strength 9 1 1 Osmotic Pressure, atm 10 1 1 ORP, volts 11 1 1 Specific Electrical Conductivity, 1/ohm-cm 12 1 1 Molar Electrical Conductivity, cm2/ohm-gmole 13 1 1 Absolute Viscosity, cP 14 1 1 Relative Viscosity 15 1 1 Vapor Compressibility 16 1 1 Mixture Heat Capacity, cal/g/K OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 23 EQSOLD – Equilibrium Information – Double Precision Numbers (continued) CALL EQSOLD (IVALR, NVALR, VEC, IERR) (Double Precision) IVALR NVALR Maximum VEC(I), I = 1 , NVALR 101 1 1 Aqueous Mass, gmoles 102 1 1 Aqueous Mass, grams 103 1 1 Aqueous Volume, m3 104 1 1 Aqueous Enthalpy, cal 105 1 1 Aqueous Density, gmole/liter 106 1 1 Aqueous Density, gram/liter 107 1 1 Aqueous Heat Capacity, cal/gram/K 201 1 1 Solid Mass, gmoles 202 1 1 Solid Mass, grams 203 1 1 Solid Volume, m3 204 1 1 Solid Enthalpy, cal 205 1 1 Solid Density, gmole/liter 206 1 1 Solid Density, gram/liter 207 1 1 Solid Heat Capacity, cal/gram/K 301 1 1 Vapor Mass, gmoles 302 1 1 Vapor Mass, grams 303 1 1 Vapor Volume, m3 304 1 1 Vapor Enthalpy, cal 305 1 1 Vapor Density, gmole/liter 306 1 1 Vapor Density, gram/liter 307 1 1 Vapor Heat Capacity, cal/gram/K 401 1 1 2nd Liquid Mass, gmoles 402 1 1 2nd Liquid Mass, grams 403 1 1 2nd Liquid Volume, m3 404 1 1 2nd Liquid Enthalpy, cal 405 1 1 2nd Liquid Density, gmole/liter 406 1 1 2nd Liquid Density, gram/liter 407 1 1 2nd Liquid Heat Capacity, cal/gram/K 408 1 1 2nd Liquid pH 409 1 1 2nd Liquid Ionic Strength 410 1 1 2nd Liquid Specific Electrical Conductivity, 1/ohm-cm 411 1 1 2nd Liquid Molar Elect Conductivity, cm2/ohm-gmole 412 1 1 2nd Liquid Absolute Viscosity, cP 413 1 1 2nd Liquid Relative Viscosity OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 24 EQSOLD – Equilibrium Information – Double Precision Numbers (continued) CALL EQSOLD (IVALR, NVALR, VEC, IERR) (Double Precision) IVALR NVALR Maximum VEC(I), I = 1 , NVALR 1001 1 1 Amount of Inflow added (FRAC) in Functions 15, 16, 17 and 18, gmole 2001 LQGSTR LQGSTR Molecular Stream Output Vector (GVEC, IGC pointers-see GVEC list; SPNAME order) 2002 LQESTR LQESTR Aqueous Stream Output Vector EVEC; see EVEC list; VNAME order) 2003 NNSOLI NNSOLI Scale Indices Output Vector (SCALE; SNAME order) 2004 NU NNSP Aqueous Stream Activity Coefficient Vector (VNAME order) 2005 NU NNSP Gibbs Free Energy of Formation, cal/gmole (VNAME order) 2006 NU NNSP Aqueous Phase Concentrations (ions and aqueous molecules only), gmole/liter (VNAME order) 2007 NU NNSP Mobilities, cm2/volt-sec (VNAME order) 2008 NU NNSP Self-Diffusivities, m2/sec (VNAME order) 2009 NU NNSP Aqueous Molar Flows (all phases), gmole (VNAME order) 2010 NU NNSP Aqueous Mass Flows (all phases), gram (VNAME order) 2011 NK NNKEQN K-Values (AKNAME order) 2012 NP NNVAP loge[2nd Liquid Phase Activities] 3001 NMOLIN NNMOLT Aqueous Stream Material Balance Flows (NAMMOL order) 3002 NMOLIN NNMOLT Solid Stream Material Balance Flows (NAMMOL order) 3003 NMOLIN NNMOLT Vapor Stream Material Balance Flows (NAMMOL order) 3004 NMOLIN NNMOLT 2nd Liquid Stream Material Balance Flows (NAMMOL order) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 25 EQSOLAD – Equilibrium Information – ASAP Variables EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN must be called before any of the Equilibrium Information calls CALL EQSOLAD (IFUNC, NVAR, AVARNAM, IVARLOC, AVARVAL, IERR) (Double Precision) Input: IFUNC = Function Number (see below for Summary) = 1 for input ASAP Variable Names (AVARNAM(I), I=1,NVAR) output ASAP Variable Locations and ASAP Values (IVARLOC(I) and AVARVAL(I), I=1,NVAR = 2 for input ASAP Variable Locations (IVARLOC(I), I=1,NVAR) output ASAP Values (AVARVAL(I), I=1,NVAR ) = 3 for input ASAP Variable Locations (IVARLOC(I), I=1,NVAR) output ASAP Variable Names and ASAP Values (AVARNAM(I) and AVARVAL(I), I=1,NVAR ) Note: Using IVARLOC is faster than using AVARNAM. The recommended procedure is to make the first call with IFUNC = 1 and IVARLOC will be returned. On subsequent calls for the same list, set IFUNC = 2. NVAR = Number of ASAP Variable values which are being requested AVARNAM(I), I=1,NVAR = ASAP variable Names (used when IFUNC = 1) (CHARACTER*16) IVARLOC(I), I=1,NVAR = ASAP variable Locations (used ONLY when IFUNC = 2 or 3) Output: AVARNAM(I), I=1,NVAR = ASAP variable Names (output when IFUNC = 3) IVARLOC(I), I=1,NVAR = ASAP variable Locations (output when IFUNC = 1) AVARVAL(I), I=1,NVAR = ASAP variable Values in ASAP Units (REAL*8) IERR = 0 No errors encountered > 1 Error(s) encountered – Number of ASAP Variable Names or Locations not found Function Summary Function Variable Names Variable Locations Variable Values IFUNC AVARNAM IVARLOC AVARVAL 1 Input Output Output 2 -- Input Output 3 Output Input Output OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 26 EQDERV – Equilibrium Information – Property Derivatives EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN must be called before any of the Derivative Information calls. This call returns the property derivatives at the composition, temperature and pressure at the converged equilibrium calculation. CALL EQDERV (IVALD, NVALD, VECOUT, IERR) Input: IVALD = ID number of property derivative to be returned (integer*4) Output: NVALD = Number of derivative values in VECOUT (integer*4) VECOUT = Vector of derivative values (REAL*8) IERR = 0 No errors encountered (integer*4) = 1 Errors IVALD NVALD VECOUT (I), I=1, NVALD 1 NU*NU D(Aqueous activity coefficient I )/D(Aqueous moles of J) 2 NU D(Aqueous activity coefficient I )/D(Temperature) 3 NU D(Aqueous activity coefficient I )/D(Pressure) 4 NU*NU D(Vapor fugacity coefficient I )/D(Vapor moles of J) 5 NU D(Vapor fugacity coefficient I )/D(Temperature) 6 NU D(Vapor fugacity coefficient I )/D(Pressure) 7 NU*4 D(Total aqueous enthalpy )/D(Aqueous moles of J) D(Total vapor enthalpy )/D(Vapor moles of J) D(Total solid enthalpy )/D(Solid moles of J) D(Total 2nd liquid enthalpy )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 8 4 D(Total aqueous enthalpy )/D(Temperature) D(Total vapor enthalpy )/D(Temperature) D(Total solid enthalpy )/D(Temperature) D(Total 2nd liquid enthalpy )/D(Temperature) 9 4 D(Total aqueous enthalpy )/D(Pressure) D(Total vapor enthalpy )/D(Pressure) D(Total solid enthalpy )/D(Pressure) D(Total 2nd liquid enthalpy )/D(Pressure) 10 NU*4 D(Total aqueous volume )/D(Aqueous moles of J) D(Total vapor volume )/D(Vapor moles of J) D(Total solid volume )/D(Solid moles of J) D(Total 2nd liquid volume )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 11 4 D(Total aqueous volume )/D(Temperature) D(Total vapor volume )/D(Temperature) D(Total solid volume )/D(Temperature) D(Total 2nd liquid volume )/D(Temperature) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 27 EQDERV – Equilibrium Information – Property Derivatives (continued) IVALD NVALD VECOUT (I), I=1, NVALD 12 4 D(Total aqueous volume )/D(Pressure) D(Total vapor volume )/D(Pressure) D(Total solid volume )/D(Pressure) D(Total 2nd liquid volume )/D(Pressure) 13 NU*4 D(Total aqueous entropy )/D(Aqueous moles of J) D(Total vapor entropy )/D(Vapor moles of J) D(Total solid entropy )/D(Solid moles of J) D(Total 2nd liquid entropy )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 14 4 D(Total aqueous entropy )/D(Temperature) D(Total vapor entropy )/D(Temperature) D(Total solid entropy )/D(Temperature) D(Total 2nd liquid entropy )/D(Temperature) 15 4 D(Total aqueous entropy )/D(Pressure) D(Total vapor entropy )/D(Pressure) D(Total solid entropy )/D(Pressure) D(Total 2nd liquid entropy )/D(Pressure) 16 NU*NU D(2nd liquid phase fugacity coefficient I )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 17 NU D(2nd liquid phase fugacity coefficient I )/D(Temperature) 18 NU D(2nd liquid phase fugacity coefficient I )/D(Pressure) Units = Heat – calories Volume – liters Moles – gram moles Temperature – C Pressure – atmosphere In all cases the component order is the full VNAME order. For derivatives where both I and J are involved I is incremented the fastest. in the VECOUT vector. Note: For option 1-3, the derivative for water is activity not activity coefficient as for all other components. OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 28 GETERR – Error Acquisition GETERRG – Error Acquisition From Generator GETERRS – Error Acquisition From Solver GETERR returns error statements resulting from GENERATE, EQMOD* or EQSOL* calls. After calling GENERATE or EQMODEL, the variable NERRORS will be returned as an argument to indicate the number of error statements in the ERROR vector. GETERR must then be called NERRORS times (IER=1, 2, …, NERRORS) to obtain each error statement in the vector ERROR which is NNERRL lines. If the variable NERRORS is not available (e.g., in the calls to EQSOL*), a call to GETERR with a value of IER which returns an IERCODE of 0 and ERROR vector blank indicates that IER error does not exist. For example, if IER=1 and GETERR returns IERCODE=0 and ERROR= ‘ ‘, then no errors occurred since the last time the Error storage was reset. To reset the Error storage, use CLRERR. CALL GETERR (IER, IERCODE, ERROR) CALL GETERRG (IER, IERCODE, ERROR) CALL GETERRS (IER, IERCODE, ERROR) Input: IER = Error number (1 to NERRORS) Output: IERCODE = Error Code Number ERROR(I), I=1,NNERRL = Error Statement Names (CHARACTER*80) CLRERR – Error Reset Resets the Error storage. Automatically called by GENERATE and EQMODEL initialization. CALL CLRERR OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 29 GETWARNG – Get Warnings From Generator GETWARNS – Get Warnings From Solver GETWARNG AND GETWARNS returns WARNING statements resulting from the execution of the generator or solver. After calling the GENERATOR or SOLVER, these routines can be called to get any warnings produced. These routines are called until IWFLAG is zero. To reset the warnings storage, use CLRERR. CALL GETWARNG (IER, IWFLAG, WARNINGS) CALL GETWARNS (IER, IWFLAG, WARNINGS) Input: None Output: IWFLAG = Warnings Code Number (IWFLAG=0 no more warnings) WARNINGS(I), I=1,NNERRL = Warnings message (CHARACTER*80) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 30 EQPROPD – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation EQMODEL must be called before any of the following calls. EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN do not need to be called. CALL EQPROPD (IVAL, VECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) (Double Precision) Input: IVAL = ID number of real number vector to be returned VECIN = Vector of real numbers describing the input for the specific IVAL (REAL*8) Output: NVECOUT = Number of real number values in vector VECOUT VECOUT = Vector of real number values (REAL*8) IERR = 0 No errors encountered = 1 Error encountered - ID not recognized IVAL VECIN VECOUT(I), I = 1 , NVECOUT 1 (1) = Temp, C (1 to NK) = loge(K-Values) (2) = Pres, atm 2 (1) = Temp,C (1) = loge(Activity) of H2O (2) = Pres, atm (2 to NU) = loge(Activity Coefficient) of (3) = H2O, gmole each –AQ and –ION species (4 to NU+2) = gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) 3 (1) = Temp,C Solid Properties (2) = blank (1) = Total Solid, gmole (3 to NI+2)= Solid, gmole (2) = Total Solid, gram (3) = Solid Enthalpy, cal (4) = Solid Density, gmole/liter (5) = Solid Density, gram/liter (6) = Solid Volume, liter 4 (1) = Location in Inflow (1) = Solute in Solution, gmole List of Solute (2) = Solute in Solution, gram (2) = blank (3 to NU+2)= Aqueous Species Moles/Molalities OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 31 EQPROPD – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation (cont.) CALL EQPROPD (IVAL, VECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) (Double Precision) IVAL VECIN VECOUT(I), I = 1 , NVECOUT 5 (1) = Location in Inflow (1) = Solute in Solution, gmole List of Solute (2) = Solute in Solution, gram (2) = blank (3 to NI+2)= Molecular Flows 6 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Liquid Density, gmole/liter (2) = Pres, atm (Does include Surface Complexation (3) = H2O, gmole Species) (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous Species gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) 7 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Liquid Absolute Viscosity, cP (2) = Pres, atm (3) = H2O, gmole (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous Species gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) 8 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Diffusivity of H2O, m2/sec (2) = Pres, atm (2 to NU) = Diffusivity of Aqueous (3) = H2O, gmole Species, m2/sec (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous Species gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) 9 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Liquid Enthalpy, cal (2) = Pres, atm (Does NOT include Surface (3) = H2O, gmole Complexation species – (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous see IVAL=23) Species gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) 10 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Vapor Enthalpy, cal (2) = Pres, atm (3) = Vapor, gmole (4 to NP+3) = Vapor Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NP+1 ) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 32 EQPROPD – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation (cont.) CALL EQPROPD (IVAL, VECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) (Double Precision) IVAL VECIN VECOUT(I), I = 1 , NVECOUT 11 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Solid Enthalpy, cal (2) = blank (3) = H2O, gmole (4 to NU+2) = all other solution species (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NU) 12 (1) = Temp,C (1) = 2nd Liquid Enthalpy, cal (2) = Pres, atm (3) = 2nd Liquid, gmole (4 to NU+3) = 2nd Liquid Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order ) For Example, NU=8 and NP=3 VNAME(1) = H2O VECIN(4) = XH2OO VNAME(2) = H2OVAP VNAME(3) = CH4VAP VNAME(4) = BENZENEVAP VNAME(5) = CH4AQ VECIN(5) = XCH4AQO VNAME(6) = BENZENEAQ VECIN(6) = XBENZENEAQO VNAME(7) = OHION VNAME(8) = HION 13 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Liquid Volume, liter (2) = Pres, atm (Does NOT include Surface (3) = H2O, gmole Complexation species – (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous see IVAL=24) Species gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) 14 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Vapor Volume, liter (2) = Pres, atm (3) = Vapor, gmole (4 to NP+3) = Vapor Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NP+1 ) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 33 EQPROPD – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation (cont.) CALL EQPROPD (IVAL, VECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) (Double Precision) IVAL VECIN VECOUT(I), I = 1 , NVECOUT 15 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Solid Volume, liter (2) = blank (3) = H2O, gmole (4 to NU+2) = all other solution species (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NU) 16 (1) = Temp,C (1) = 2nd Liquid Volume, liter (2) = Pres, atm (3) = 2nd Liquid, gmole (4 to NU+3) = 2nd Liquid Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order ) For Example see Option 12 17 (1) = Temp,C (1 to NP) = loge(Vapor Fugacity Coefficient) (2) = Pres, atm of each –VAP (3) = Vapor, gmole (4 to NP+3) = Vapor Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NP+1 ) 18 (1) = Temp,C (1 to NU) = loge(2nd Liquid Fugacity) (2) = Pres, atm of XH2OO and each X–AQO (3) = 2nd Liquid, gmole (4 to NU+3) = 2nd Liquid Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order) For Example see Option 12 19 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Liquid Entropy, cal/C (2) = Pres, atm (2) = Liquid Gibbs Free Energy, cal (3) = H2O, gmole (3) = Liquid Enthalpy, cal (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous Species gmoles (–AQ and –ION only) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 34 EQPROPD – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation (cont.) CALL EQPROPD (IVAL, VECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) (Double Precision) IVAL VECIN VECOUT(I), I = 1 , NVECOUT 20 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Vapor Entropy, cal/C (2) = Pres, atm (2) = Vapor Gibbs Free Energy, cal (3) = Vapor, gmole (3) = Vapor Enthalpy, cal (4 to NP+3) = Vapor Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NP+1 ) 21 (1) = Temp,C (1) = 2nd Liquid Entropy, cal/C (2) = Pres, atm (2) = 2nd Liquid Gibbs Free Energy, cal (3) = 2nd Liquid, gmole (3) = 2nd Liquid Enthalpy, cal (4 to NU+3) = 2nd Liquid Species Mole Fractions (VNAME order) For Example see Option 12 22 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Solid Entropy, cal/C (2) = blank (2) = Solid Gibbs Free Energy, cal (3) = H2O, gmole (3) = Solid Enthalpy, cal (4 to NU+2) = all other solution species (VNAME order, EVEC locations 2 to NU) 23 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Enthalpy of Surface Complexation (2) = Pres, atm species in Aqueous Phase, cal (3) = H2O, gmole (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous Species gmoles (–CPI and –CPM) 24 (1) = Temp,C (1) = Volume of Surface Complexation (2) = Pres, atm species in Aqueous Phase, liter (3) = H2O, gmole (4 to NU+2) = Aqueous Species gmoles (–CPI and –CPM) 25 (1)=Temp,C (1 to NU) Standand State Gibbs Free Energy (2)=Pres,atm cal/mole OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 35 EQPROPD – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation (cont.) CALL EQPROPD (IVAL, VECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) (Double Precision) EQPROPD Input Summary
VECIN Locations -------------------------
IVAL VECIN(1) VECIN(2) VECIN(3) VECIN(4) VECIN(5 to …) 1 Temp Pres 2 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 3 Temp -- Solid(1) Solid(2) Solid(3 to NI) 4 Location in -- EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) inflow list of solute 5 Location in -- GVEC(1) GVEC(2) GVEC(3 to NI) inflow list of solute 6 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 7 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 8 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 9 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 10 Temp Pres Vapor EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NP+1) 11 Temp -- EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 12 Temp Pres 2nd Liquid EVEC(NNSP+6) EVEC(NNSP+7 to NNSP+5+NU) 13 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 14 Temp Pres Vapor EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NP+1) 15 Temp -- EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 16 Temp Pres 2nd Liquid EVEC(NNSP+6) EVEC(NNSP+7 to NNSP+5+NU) 17 Temp Pres Vapor EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NP+1) 18 Temp Pres 2nd Liquid EVEC(NNSP+6) EVEC(NNSP+7 to NNSP+5+NU) 19 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 20 Temp Pres Vapor EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NP+1) 21 Temp Pres 2nd Liquid EVEC(NNSP+6) EVEC(NNSP+7 to NNSP+5+NU) 22 Temp -- EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 23 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) 24 Temp Pres EVEC(1) EVEC(2) EVEC(3 to NU) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 36 EQPROP – Properties Computation without Equilibrium Calculation EQPROP performs the same calculations as EQPROPD with different input parameters. The output is the same as EQPROPD. EQMODEL must be called before any of the following calls. EQSOLVED, EQSOLVEP, EQSOLVFD or EQLABAN do not need to be called. CALL EQPROP (IVAL, TEMP, PRES, EVECIN, NVECOUT, VECOUT, IERR) Input: IVAL = ID number of real number vector to be returned (See EQPROPD) TEMP = Temperature, C PRES = Pressure, atm EVECIN = EVEC input vector in vname order. Output See EQPROPD output OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 37 EQPRDERV – Property Derivatives without Equilibrium EQMODEL must be called before any of the Derivative Information calls. This call returns the property derivatives at the user specified composition, temperature and pressure. CALL EQPRDERV (IDERV, TEMP, PRES, EVECIN, NVALD, VECOUT, IERR) Input: IDERV = ID number of property derivative to be returned (integer*4) TEMP = Temperature, C PRES = Pressure, atm EVECIN = EVEC input vector in vname order Output: NVALD = Number of derivative values in VECOUT (integer*4) VECOUT = Vector of derivative values (REAL*8) IERR = 0 No errors encountered (integer*4) = 1 Errors IVALD NVALD VECOUT (I), I=1, NVALD 1 NU*NU D(Aqueous activity coefficient I )/D(Aqueous moles of J) 2 NU D(Aqueous activity coefficient I )/D(Temperature) 3 NU D(Aqueous activity coefficient I )/D(Pressure) 4 NU*NU D(Vapor fugacity coefficient I )/D(Vapor moles of J) 5 NU D(Vapor fugacity coefficient I )/D(Temperature) 6 NU D(Vapor fugacity coefficient I )/D(Pressure) 7 NU*4 D(Total aqueous enthalpy )/D(Aqueous moles of J) D(Total vapor enthalpy )/D(Vapor moles of J) D(Total solid enthalpy )/D(Solid moles of J) D(Total 2nd liquid enthalpy )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 8 4 D(Total aqueous enthalpy )/D(Temperature) D(Total vapor enthalpy )/D(Temperature) D(Total solid enthalpy )/D(Temperature) D(Total 2nd liquid enthalpy )/D(Temperature) 9 4 D(Total aqueous enthalpy )/D(Pressure) D(Total vapor enthalpy )/D(Pressure) D(Total solid enthalpy )/D(Pressure) D(Total 2nd liquid enthalpy )/D(Pressure) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 38 EQPRDERV – Property Derivatives without Equilibrium (continued) IVALD NVALD VECOUT (I), I=1, NVALD 10 NU*4 D(Total aqueous volume )/D(Aqueous moles of J) D(Total vapor volume )/D(Vapor moles of J) D(Total solid volume )/D(Solid moles of J) D(Total 2nd liquid volume )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 11 4 D(Total aqueous volume )/D(Temperature) D(Total vapor volume )/D(Temperature) D(Total solid volume )/D(Temperature) D(Total 2nd liquid volume )/D(Temperature) 12 4 D(Total aqueous volume )/D(Pressure) D(Total vapor volume )/D(Pressure) D(Total solid volume )/D(Pressure) D(Total 2nd liquid volume )/D(Pressure) 13 NU*4 D(Total aqueous entropy )/D(Aqueous moles of J) D(Total vapor entropy )/D(Vapor moles of J) D(Total solid entropy )/D(Solid moles of J) D(Total 2nd liquid entropy )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 14 4 D(Total aqueous entropy )/D(Temperature) D(Total vapor entropy )/D(Temperature) D(Total solid entropy )/D(Temperature) D(Total 2nd liquid entropy )/D(Temperature) 15 4 D(Total aqueous entropy )/D(Pressure) D(Total vapor entropy )/D(Pressure) D(Total solid entropy )/D(Pressure) D(Total 2nd liquid entropy )/D(Pressure) 16 NU*NU D(2nd liquid phase fugacity coefficient I )/D(2nd liquid moles of J) 17 NU D(2nd liquid phase fugacity coefficient I )/D(Temperature) 18 NU D(2nd liquid phase fugacity coefficient I )/D(Pressure) Units = Heat – calories Volume – liters Moles – gram moles Temperature – C Pressure – atmosphere In all cases the component order is the full VNAME order. For derivatives where both I and J are involved I is incremented the fastest. in the VECOUT vector. Note: For option 1-3, the derivative for water is activity not activity coefficient as for all other components. OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 39 GVEC – Molecular Stream Description GVEC(I), I = 1 , LQGSTR (For NNIN=300, LQGSTR=1280) Element Number(s) Current IGC Entry I = IGC(1)+1, IGC(1)+300 = 1,300 Molecular, aqueous liquid, gmole = IGC(2)+1 = 301 Total, gmole = +2 = 302 Temperature, C = +3 = 303 Pressure, atm = +4 = 304 Enthalpy, cal = +5 = 305 Density, gmole/liter = +6 = 306 pH = +7 = 307 Ionic strength, molality = +8 = 308 Volume, m3 = +9 = 309 Osmotic pressure, atm = +10 = 310 Mass, gram = +11 = 311 Heat capacity, cal/g/K = +12 = 312 ORP, volt = +13 = 313 Specific Electrical Conductivity, 1/ohm-cm = +14 = 314 Molar Electrical Conductivity, cm2/ohm-gmole = +15 = 315 Absolute Viscosity, cP = +16 = 316 Relative Viscosity = ……. = +20 = 320 = IGC(3)+1, IGC(3)+300 = 321,620 Molecular, solids, gmole = IGC(4)+1 = 621 Total flow, gmole = +2 = 622 Temperature, C = +3 = 623 Pressure, atm = +4 = 624 Enthalpy, cal = +5 = 625 Density, gmole/liter = +6 = 626 = +7 = 627 = +8 = 628 Volume, m3 = +9 = 628 = +10 = 630 Mass, gram = +11 = 631 Heat capacity, cal/g/K = +12 = 632 = +13 = 633 = +14 = 634 = +15 = 635 = +16 = 636 = ……. = +20 = 640 =IGC(5)+1, IGC(5)+300 = 641,940 Molecular Vapor = IGC(6)+1 = 941 Total flow, gmole = +2 = 942 Temperature, C = +3 = 943 Pressure, atm = +4 = 944 Enthalpy, cal = +5 = 945 Density, gmole/liter = +6 = 946 = +7 = 947 = +8 = 948 Volume, m3 = +9 = 949 = +10 = 950 Mass, gram = +11 = 951 Heat capacity, cal/g/K = +12 = 932 = +13 = 933 = +14 = 954 = +15 = 955 = +16 = 956 = ……. = +20 = 960 OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 40 = IGC(7)+1, IGC(7)+300 = 961,1260 Molecular, 2nd liquid, gmole = IGC(8)+1 = 1261 Total, gmole = +2 = 1262 Temperature, C = +3 = 1263 Pressure, atm = +4 = 1264 Enthalpy, cal = +5 = 1265 Density, gmole/liter = +6 = 1266 pH = +7 = 1267 Ionic strength = +8 = 1268 Volume, m3 = +9 = 1269 = +10 = 1270 Mass, gram = +11 = 1271 Heat capacity, cal/g/K = +12 = 1272 ORP, volt = +13 = 1273 Specific Electrical Conductivity, 1/ohm-cm = +14 = 1274 Molar Electrical Conductivity, cm2/ohm-gmole = +15 = 1275 Absolute Viscosity, cP = +16 = 1276 Relative Viscosity = ……. = +20 = 1280 = IGC(10)+1 = 1281 = +2 = 1282 Total Mass, gmole = +3 = 1283 Total Volume, m3 = +4 = 1284 = +5 = 1285 Total Mass, gram = +6 = 1286 Total Enthalpy, cal = +7 = 1287 = +8 = 1288 = +9 = 1289 = +10 = 1280 = +11 = 1281 Mixture Heat capacity, cal/g/K OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 41 GVEC – Molecular Stream Description (continued) GVEC(I), I = 1 , LQGSTR (For NNIN=300, LQGSTR=1280) Element Number(s) Current IGC Entry I = IGC(11)+1 = 1251 = +2 = 1252 = +3 = 1253 = +4 = 1254 = +5 = 1255 = +6 = 1256 Vapor Compressibility Factor (z) = +7 = 1257 = +8 = 1258 = +9 = 1259 = +10 = 1260 = +11 = 1261 Crystallization – Zeroth Moment, m0, 1/cm3 = +12 = 1262 Crystallization – First Moment, m1, cm/cm3 = +13 = 1263 Crystallization – Second Moment, m2, cm2/cm3 = +14 = 1264 Crystallization – Third Moment, m3, cm3/cm3 = +15 = 1265 Crystallization – Fourth Moment, m4, cm4/cm3 = +16 = 1266 Crystallization – Fifth Moment, m5, cm5/cm3 = +17 = 1267 Crystallization – Specific Surface Area, AT, cm2/cm3 = +18 = 1268 Crystallization – Crystal Mass Density, MT, gm/cm3 = +19 = 1269 Crystallization – Area Shape Factor, kA = +20 = 1270 Crystallization – Volume Shape Factor, kV = +21 = 1271 Crystallization – Density of Crystals, gm/cm3 = +22 = 1272 = +23 = 1273 = +24 = 1274 = +25 = 1275 = +26 = 1276 = +27 = 1277 = +28 = 1278 = +29 = 1279 = +30 = 1280 Crystal Size Distribution (CSD) = IGC(12)+1 = 1281 Number of Crystal Size Categories (NSIZE) = +2 = 1282 Size of Crystal, Category 1, micron = +3 = 1283 Crystal Size Distribution, Size 1, number/cm3-micron = +4 = 1284 Size of Crystal, Category 2, micron = +5 = 1285 Crystal Size Distribution, Size 2, number/cm3-micron
- : : : : : :
- : : : : : :
= +2*NSIZE = 1280+2*NSIZE Size of Crystal, Category NSIZE, micron = +2*NSIZE+1 = 1281+2*NSIZE Crystal Size Distribution, Size NSIZE, number/cm3-micron OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 42 EVEC – Aqueous Stream Description EVEC(I), I = 1 , LQESTR (For NNSP=300, LQESTR=610) I = 1 H2O in aqueous phase, gmole = 2,NU Species quantity in aqueous phase, –AQ, –ION - gmole –PPT, –.nH2O, –SUS, –LT - gmole –VAP - mole fraction –SOL - gmole/kg solid medium –CPI, –CPM - gmole/kg H2O = NNSP+1 Temperature, K = NNSP+2 Pressure, atm = NNSP+3 Vapor, gmole = NNSP+4 Total Aqueous (H2O, –AQ, –ION), gmole = NNSP+5 SOLMAS, kg = NNSP+6,NNSP+5+NU Species concentration in organic phase, mole fraction = NNSP+5+NNSP+1 Total Organic, gmole = NNSP+5+NNSP+2 SELIM OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 43 ASAP Units Variable Name Value Units T temperature Kelvin PT pressure atmosphere I ionic strength gmole/kg H2O PH pH -- OSPRES osmotic pressure atmosphere ORP oxidation reduction potential volt ECOND specific electrical conductivity 1/ohm-cm ECONDM molar electrical conductivity cm2/ohm-gmole VISABS absolute viscosity cP VISREL relative viscosity –IN inflows gmole –AQ, –ION aqueous solutions mole fractions –CPM, –CPI surface complex mole fractions –PPT, –.nH2O precipitates and hydrates gmole –SUS suspended phase solids gmole –LT lattice species (coprecipitation) gmole H2O water in solution mole fraction –SOL solid solution molalities gmol/kg solid medium Y– vapor mole fractions -- X–O 2nd liquid phase mole fractions -- D_H2O diffusivity, water m2/sec D_–AQ, –ION diffusivities, aqueous species m2/sec SOLMAS solid medium mass kg Note: For cation exchange medium, SOLMAS based upon H-Solid molecular weight. LIQMAS total aqueous liquid mass gram LIQMAS2 total organic phase mass gram LIQMOL total aqueous liquid moles gmole V total vapor moles gmole SOLMOL total solid moles gmole TOTO total organic liquid moles gmole ENTHALPY total enthalpy cal ENTHAL aqueous liquid phase enthalpy cal ENTHAL2 organic liquid phase enthalpy cal ENTHAV vapor phase enthalpy cal ENTHAS solid phases enthalpy cal ENTHAI inert phases enthalpy cal DENLIQ aqueous liquid molar density gmole in soln/liter DENLIQ2 organic liquid molar density gmole in soln/liter DENMAS aqueous liquid density gram/liter DENMAS2 organic liquid density gram/liter ZCOMP vapor compressibility -- ASAP Units (continued) OLI Systems, Inc. OLI Engine 9.1 Reference Manual Page 44 Variable Name Value Units VOL total volume liter VOLLIQ aqueous liquid volume liter VOLLIQ2 organic liquid volume liter VOLVAP vapor volume liter VOLSOL solid volume liter RATEi kinetics rate of reaction, reaction i gmole/hr EXTi kinetics extent of reaction, reaction i gmole TSTEP kinetics time step hr BRATESi rate of reaction – synthesis, bioreaction i gmole/liter-hr BEXTSi extent of reaction – synthesis, bioreaction i gmole BRATEEAi rate of reaction – aerobic energy, bioreaction i gmole/liter-hr BEXTEAi extent of reaction – aerobic energy, bioreaction I gmole BRATEENi rate of reaction – anoxic energy, bioreaction i gmole/liter-hr BEXTENi extent of reaction – anoxic energy, bioreaction I gmole BRATEECi rate of reaction – anaerobic energy, bioreaction i gmole/liter-hr BEXTECi extent of reaction – anaerobic energy, bioreaction I gmole BRATDEAi rate of reaction – aerobic decay, bioreaction i gmole/liter-hr BEXTDAi extent of reaction – aerobic decay, bioreaction I gmole BRATDENi rate of reaction – anoxic decay, bioreaction i gmole/liter-hr BEXTDNi extent of reaction – anoxic decay, bioreaction i gmole REACVOL bioreactor volume liter A–AQ, A–ION loge (aq phase activity coef) -- A–CPM, A–CPI loge (aq phase activity coef) -- AH2O loge (aq phase H2O activity coef) -- A–AQO loge (organic phase activity coef) -- AY– loge (vapor phase fugacity coef) -- K- loge (equilibrium K-values) -- L–AQ, L–ION loge (aq phase mole fraction) -- L–CPM, L–CPI loge (aq phase mole fraction) --